From Docker Compose to GitOps: Managing Nextcloud with FluxCD & K3s
How I moved my Nextcloud setup from Docker Compose to K3s by using FluxCD and overlays. I'll walk you through my GitOps flow of syncing from GitHub, managing credentials with sealed secrets and automate the deployment.

This post has been updated due to changes in some of the YAML files. Scroll to the bottom for a detailed changelog.
For the longest time I have been using Docker Compose. It's simple, familiar, and gets the job done. But I wanted to make the switch to Kubernetes and automate the deployments. This is where k3s, a lightweight Kubernetes Distro comes in. In this article I will explain how I manage my Nextcloud deployment with FluxCD and Overlays.
FluxCD is a GitOps tool that enables us to sync git repositories into our cluster. The idea is to put our manifests in a git repository, and structuring the repo in a monorepo approach. You commit changes to this repository and Flux will sync them to the cluster.
FluxCD Kustomization is used to tell FluxCD how to apply the Kubernetes manifest stored in our monorepo. It is a central component for our Flux GitOps workflow as it will tell Flux where to find the manifests, how to deploy them and how often to check for updates.
In my Nextcloud deployment example, the Kustomization resource will target the overlay directory (./apps/overlays/rudolf/nextcloud) and make sure that all Nextcloud resources located in the base directory (./apps/base/nextcloud/) are deployed in the targetNamespace: rudolf-nextcloud and ensure they are configured with the correct credentials from the rudolf-nextcloud-sealed-secret.
I won't bore you to sleep with installing k3s and bootstrapping FluxCD, but you will need a Kubernetes Cluster with FluxCD bootstrapped for GitHub and Bitnami’s sealed-secrets controller to store secrets safely.
GitOps Workflow Overview
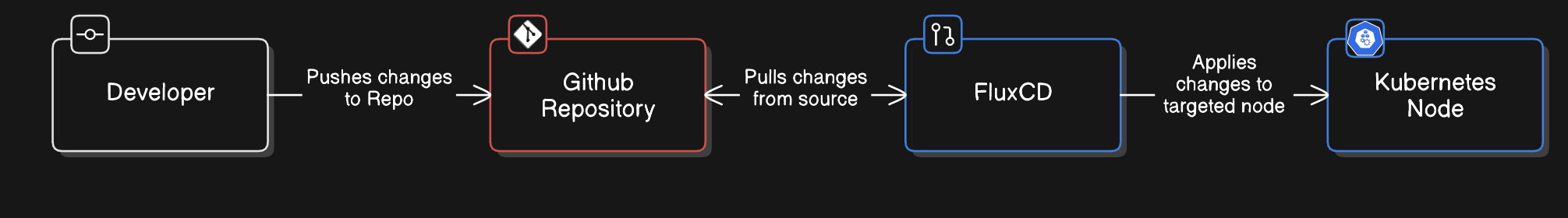
Here is a brief simplified explanation on my GitOps Workflow works. FluxCD is running on my k3s cluster:
| Role | Node Name |
|---|---|
| Control Plane | node1-gryffyndor |
| Worker | node2-ravenclaw |
| Worker | node3-hufflepuff |
| Worker | node4-slytherin |
FluxCD monitors my Github Repository for changes. It will compare and adjust the state of the Kubernetes cluster. This process is called Reconciliation and allows FluxCD to carry out the configuration found in the Github Repository.
Monorepo
To manage Nextcloud deployments I will use a monorepo approach outlined by FluxCD. These are the main components I used for a Nextcloud installation on Kubernetes:
- Database: MySQL, MariaDB or PostgreSQL
- Redis: Caching and Transactional file locking
- Nextcloud
The database, Nextcloud and Redis service will have its own PersistentVolumeClaim and Service. The configurations all reference the same SealedSecret called nextcloud-mariadb-secret. This SealedSecret is located in the overlays directory and customized for each client or environment.
The base folder holds YAML installation configuration, like deployment.yaml, service.yaml. The YAML files stored in this directory will not have a namespace in their metadata.
The overlays folder contains environment-specific overlays, like namespace and database variables such as username and passwords that are stored in a sealed secret.
├── apps
│ └── base
│ └── nextcloud
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-deployment.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-mariadb.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-nextcloud.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-pvc-db.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-pvc-nc.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-pvc-redis.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-redis.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-svc-db.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-svc-nc.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-svc-redis.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-volume.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-cert.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-ingress.yaml
│ └── nextcloud-cron.yaml
└── overlays
├── rudolf
│ └── nextcloud
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ ├── nextcloud-namespace.yaml
│ └── nextcloud-sealed-secret.yaml
└── other
└── nextcloud
├── kustomization.yaml
├── nextcloud-namespace.yaml
└── nextcloud-sealed-secret.yaml
Securing Secrets with Sealed Secrets
The heart of this deployment revolves around the SealedSecret. We start by creating an Opaque Secret that contains sensitive information like database credentials and admin passwords. Here’s an example of what the unencrypted secret looks like:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: nextcloud-mariadb-secret
namespace: rudolf-nextcloud
type: Opaque
stringData:
mysql-host: mariadb.rudolf-nextcloud.svc.cluster.local
mysql-database: nextcloud
mysql-user: nextcloud
mysql-password: MYSQLPASSWORD
redis-host: redis.rudolf-nextcloud.svc.cluster.local
nextcloud_admin_user: rudolf
nextcloud_admin_password: ADMINPASSWORD
This Secret contains the following fields:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
mysql-host |
Hostname of the MariaDB server |
mysql-database |
Name of the Nextcloud database |
mysql-user |
Username for the MariaDB database |
mysql-password |
Password for the MariaDB user |
redis-host |
Hostname of the Redis server |
nextcloud_admin_user |
Username for the Nextcloud admin account |
nextcloud_admin_password |
Password for the Nextcloud admin account |
To secure this secret in Git, we encrypt it using kubeseal, that is included in the sealed-secrets controller. First, find your the controller’s public key (certificate) with:
kubeseal --fetch-cert > controller-cert.pem
Then, use kubeseal to encrypt the secret:
kubeseal --cert=/home/rudolf/controller-cert.pem < nextcloud-secret.yaml > nextcloud-sealed-secret.yaml
This creates a SealedSecret that can safely be committed to your Git repository. The SealedSecret and Secret must have the same namespace and name, as the sealed-secrets controller uses this information to correctly map and decrypt the secret when applying it to your cluster.
Important: Once you’ve created the
SealedSecret, delete the originalSecretfile to avoid accidentally exposing sensitive information.
Deployment
Step 1: FluxCD GitRepository
To deploy Nextcloud using FluxCD will we need to tell Flux where to pull the Kubernetes manifests from. It connects my k3s cluster to a Git repository, therefore acting as the source of truth for all the configurations that FluxCD will apply and manage.
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: GitRepository
metadata:
name: rudolf-nextcloud-repo
namespace: default
spec:
interval: 1m
url: https://github.com/rud3olph/hogwarts
ref:
branch: main
secretRef:
name: git-access-auth
This GitRepository resource does the following:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
url |
Points FluxCD to the GitHub repository containing the Nextcloud manifests |
interval: 1m |
Tells Flux to check for changes every minute |
ref |
Ensures Flux tracks the main branch |
secretRef |
Allows Flux to authenticate securely if the repository is private |
Step 2: FluxCD Kustomization
Now we have to define how FluxCD should apply these Kubernetes manifests stored in the GitRepository to the k3s cluster.
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: rudolf-nextcloud-kustomization
namespace: default
spec:
interval: 1m
targetNamespace: rudolf-nextcloud
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: rudolf-nextcloud-repo
path: "./apps/overlays/rudolf/nextcloud"
prune: true
wait: true
timeout: 1m
This Kustomization resource does the following:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
name |
Unique identifier for the FluxCD Kustomization |
namespace |
Namespace where the Kustomization resource is created (default) |
interval |
How often Flux checks for repository changes (1 minute) |
targetNamespace |
Destination namespace for deployed resources (rudolf-nextcloud) |
sourceRef |
Reference to the GitRepository source (rudolf-nextcloud-repo) |
path |
Repository path containing manifests (./apps/overlays/rudolf/nextcloud) |
Step 3: Kustomize processes Resources in Order
Kubernetes Kustomize will start deploying the listed resources after apply both the FluxCD Gitrepository and Kustomization:
| File/Path | Purpose |
|---|---|
rudolf-nextcloud-namespace.yaml |
Creates the namespace for Nextcloud deployment |
rudolf-nextcloud-sealed-secret.yaml |
Deploys the SealedSecret containing credentials |
../../../base/nextcloud |
References the base kustomization.yaml to apply standard Nextcloud configurations |
Base Resources:
Click to expand: nextcloud-mariadb.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: mariadb
spec:
serviceName: "mariadb"
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mariadb
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mariadb
spec:
containers:
- name: mariadb
image: mariadb:10.11
env:
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nextcloud-mariadb-secret
key: mysql-password
- name: MYSQL_DATABASE
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nextcloud-mariadb-secret
key: mysql-database
- name: MYSQL_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nextcloud-mariadb-secret
key: mysql-user
- name: MYSQL_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nextcloud-mariadb-secret
key: mysql-password
- name: REDIS_HOST
value: redis
ports:
- containerPort: 3306
resources:
requests:
memory: "4Gi"
cpu: "250m"
volumeMounts:
- name: mariadb-data
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
volumes:
- name: mariadb-data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mariadb-pvc
nodeSelector:
node-role: worker-slytherin
Click to expand: nextcloud-pvc-db.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: mariadb-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 20Gi
Click to expand: nextcloud-svc-db.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mariadb
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 3306
targetPort: 3306
selector:
app: mariadb
Click to expand: nextcloud-redis.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: redis
spec:
serviceName: "redis"
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: redis
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: redis
spec:
containers:
- name: redis
image: redis:7.4.2
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
resources:
requests:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: "250m"
volumeMounts:
- name: redis-data
mountPath: /data
volumes:
- name: redis-data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: redis-pvc
nodeSelector:
node-role: worker-slytherin
Click to expand: nextcloud-pvc-redis.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: redis-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi
Click to expand: nextcloud-svc-redis.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: redis
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 6379
targetPort: 6379
selector:
app: redis
Click to expand: nextcloud-nextcloud.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nextcloud
spec:
serviceName: "nextcloud"
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nextcloud
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nextcloud
spec:
containers:
- name: nextcloud
image: nextcloud:apache
imagePullPolicy: Always
env:
- name: MYSQL_HOST
value: mariadb
- name: MYSQL_DATABASE
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nextcloud-mariadb-secret
key: mysql-database
- name: MYSQL_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nextcloud-mariadb-secret
key: mysql-user
- name: MYSQL_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nextcloud-mariadb-secret
key: mysql-password
- name: NEXTCLOUD_ADMIN_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nextcloud-mariadb-secret
key: nextcloud_admin_user
- name: NEXTCLOUD_ADMIN_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nextcloud-mariadb-secret
key: nextcloud_admin_password
- name: NEXTCLOUD_TRUSTED_DOMAINS
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: nextcloud-mariadb-secret
key: nextcloud_trusted_domains
- name: OVERWRITEPROTOCOL
value: https
- name: REDIS_HOST
value: redis
- name: REDIS_PORT
value: "6379"
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
memory: "8Gi"
cpu: "500m"
volumeMounts:
- name: nextcloud-data
mountPath: /var/www/html
volumes:
- name: nextcloud-data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: nextcloud-pvc
nodeSelector:
node-role: worker-slytherin
Click to expand: nextcloud-pvc-nc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: nextcloud-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
Click to expand: nextcloud-svc-nc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nextcloud
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nextcloud
Click to expand: nextcloud-volume.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: nc-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 500Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
storageClassName: local-storage
local:
path: /home/rudolf/nc
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node-role
operator: In
values:
- worker-slytherin
Click to expand: nextcloud-cert.yaml
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: nextcloud-tls
spec:
secretName: nextcloud-tls
issuerRef:
name: letsencrypt-dns
kind: ClusterIssuer
dnsNames:
- nextcloud.roomofrequirement.nl
Click to expand: nextcloud-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nextcloud
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx"
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt-dns"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: "10G"
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
tls:
- hosts:
- nextcloud.roomofrequirement.nl
secretName: nextcloud-tls
rules:
- host: nextcloud.roomofrequirement.nl
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nextcloud
port:
number: 80
Click to expand: nextcloud-cron.yaml
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: nextcloud-cron
spec:
schedule: "*/5 * * * *"
successfulJobsHistoryLimit: 3
failedJobsHistoryLimit: 1
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: nextcloud-cron
image: nextcloud:apache
command: ["php", "-f", "/var/www/html/cron.php"]
resources:
requests:
cpu: "256m"
memory: "1Gi"
securityContext:
runAsUser: 33
runAsGroup: 33
volumeMounts:
- name: nextcloud-pvc
mountPath: /var/www/html
restartPolicy: OnFailure
volumes:
- name: nextcloud-pvc
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: nextcloud-pvc
Step 4: Completing the setup
Once Nextcloud is deployed you can check if the Memory caching has been configured correctly by visiting Administration > Overview > Security & setup warnings
Check for:
- Cache warnings: “No memory cache has been configured. To enhance your performance please configure a memcache if available.”
- Transactional file: “Transactional file locking is disabled, this might lead to issues with race conditions.”
If these warnings show up you can turn to the Nextcloud configuration / Memory caching documentation
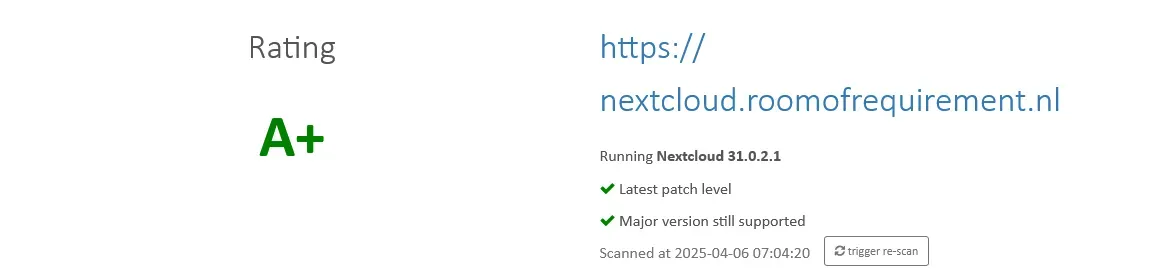
Lastly you can use the Nextcloud Security Scan to see if your installation is up to date and well secured.
Changelog:
19-06-2025
Major updates:
- Changed Nextcloud
StatefulSettoDeployment - Changed NodePort to
ClusterIPforingres-ngnix - Changed nodeSelector from worker-ravenclaw to worker-slytherin
- Added nextcloud-volume.yaml for local-storage access
- Added backgroundjob: nextcloud-cron.yaml
- Added certificate: nextcloud-cert.yaml
- Added ingress: nextcloud-ingress.yaml
Minor updates:
- Updated k3s cluster overview, added worker: node4-slytherin
- Changed nextcloud dashboard image after completing the setup